
Credit: C. Burrows
(ESA/STScI), HST,NASA
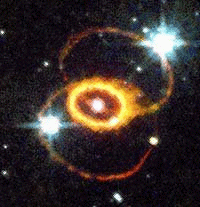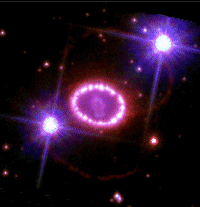
The origin of the rings remains a mystery.
Astronomy Picture of the Day July 5, 1996

The outer rings are faintly
visible in this image.
SN 1987a Blink Comparator
|
This article has the following sections. A Ritzian Interpretation of Variable Stars Non-pulsating Cepheid Variables Ritzian Gamma-Ray Bursts Ultra High Energy Cosmic Rays Modeling Geminga Unsung Binaries and de Sitter's Whimsical Images? GRB 790731 and omega Geminorum Unsung Binaries and de Sitter's Whimsical Images?Shade Tree PhysicsLatest Update 02 Mar 2018.New or modified material is in bold. This page presents a collection of stellar images that might be showing binaries where they wern't suspected to be such, and evidence of Ritzian c+v arrival time modulation for binary stars (also not thought to be such). (The time modulation sometimes allows a component of a binary star to be seen on opposite sides of the component's orbit at the same time. In each example the seeing of the detecting instrument is thought to be sufficient to resolve the separated images.
Mira Ceti has been removed from this page because
* * *
|
|
|

The outer rings are faintly visible in this image. |

SN 1987a Blink Comparator |
|
* * * |

SS443 Link was: http://cosmic.riken.go.jp/kotani/SS443 ASCA GIS (X-Ray) Reported as having two sets of moving X-ray lines. |
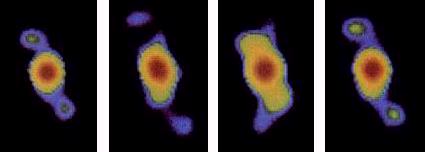
Sequential false-color radio images of SS-433, made with the Very Large Array, in January, February, March, and April of 1981. (VLA/NRAO). According to the Ritzian hypothesis the features that have been identified as jets would be interpreted as de Sitter images (of a binary component) that are periodically seen simultaneously on opposite sides of the binary center-of-gravity.
* * * Super Nova 2006gy
Chandra X-Ray / Lick IR Credit: Illustration: NASA/CXC/M. Weiss: X-ray: NASA/CXC/ UC Berkeley/N. Smith et al.; IR: Lick/UC Berkeley/J. Bloom & C. Hansen See: |